Does not burn fuel directly, which contributes to greenhouse gas reduction
Renewable Energy
Introduction to Apt Neuroscience's Geothermal heating and cooling system
Definition of Geothermal Energy

The 'New Energy and Renewable Energy Development,
Use and Dissemination Promotion Act' enacted
by the Ministry of Industry and Trade specifies
geothermal energy as one of renewable energy,
and the Enforcement Rule of the same Act defines
'geothermal energy facilities: facilities that produce energy
by converting the temperature difference between
water, groundwater, and underground heat.'
Nature of geothermal energy
Since geothermal energy can be developed and utilized regardless of weather or climatic conditions, it is the only renewable energy source in charge of baseload,
characterized by easy output adjustment according to load conditions.
Utilization of geothermal energy and classification of technology
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
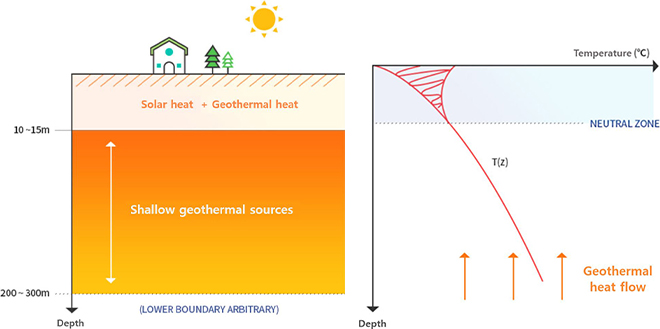
- It is classified into deep geothermal heat and shallow geothermal heat depending on the depth of use of geothermal energy.
- Deep geothermal heat uses geothermal water at a depth of more than 300m underground or heat from high bedrock
- Shallow geothermal heat uses the temperature difference between the temperature of the atmosphere and the subsurface temperature that is constant throughout the year within a depth of 300m underground
- In Korea, shallow geothermal heat using a geothermal source heat pump is mainly used.
Basic principles of geothermal heat
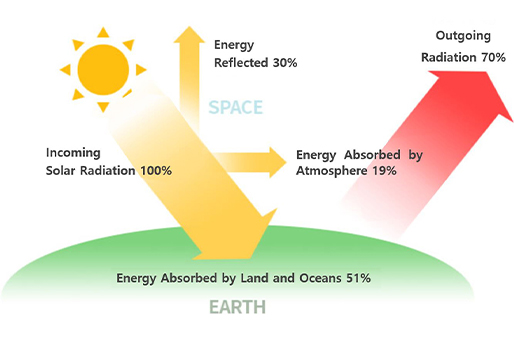
- 51% of the sun's heat is absorbed by the surface and sea level (500 times the amount of energy used by humanity)
- The underground temperature of 20 ~ 200 m underground maintains a constant temperature (15℃)
- It rises by 2.5℃/100 m below 200 m underground
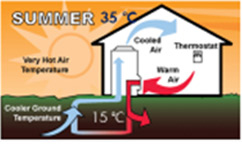
- Geothermal heating and cooling system uses underground temperature (15℃)
- Energy from seawater, rivers, groundwater and lakes is also included in geothermal energy.
- Geothermal heat is "renewable energy" that can be used indefinitely.
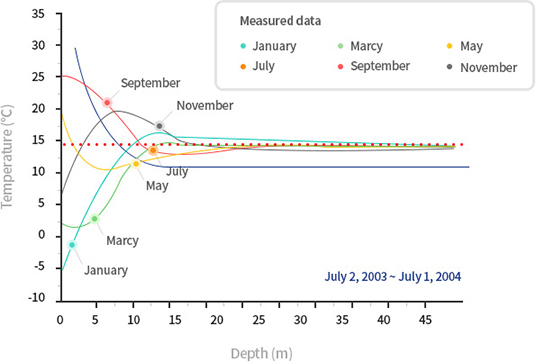
Geothermal excellence

It is a system used for cooling, heating, and hot water supply by configuring a refrigeration cycle with a heat pump with the underground temperature (usually 15 ± 5 ℃) maintained constant throughout the year under 10m underground, which is an eco-friendly heating and cooling system with high economic feasibility that dramatically reduces energy costs.Extracting geothermal heat or using a circulation circuit installed in the ground to dissipate the heat extracted from the inside to the ground, Geothermal heating and cooling systems absorb or dissipate geothermal heat from the ground. It is also the most efficient and environmentally friendly heating and cooling system certified by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Classification of geothermal heating and cooling systems
An open system that directly uses groundwater in a geothermal heating and cooling system is superior in efficiency, but securing the required amount of groundwater everywhere isn't easy. The closed system uses the ground heat stored in the ground as a heat source, buries pipes made of HDPE, etc., in the ground, forms a closed circuit system, fills the inside with fluid, and allows the circulating fluid to exchange heat for absorbing or releasing heat to achieve heating and cooling. In the domestic environment, closed geothermal systems are more widely used than open geothermal systems.
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
| Circuit type | System type | Heat source |
|---|---|---|
| Open geothermal system |
|
shallow geothermal heat, groundwater, seawater and surface water |
| Closed geothermal system |
|
shallow geothermal heat, groundwater and surface water |
| Complex geothermal heat pump system |
A geothermal heat pump system linked to an existing cooling tower or boiler. |
shallow geothermal heat, groundwater, existing heating and cooling facilities |
Advantages
- No loss of circulating water as it circulates in a closed circuit.
- Minimized problems such as scale and corrosion.
- Closed type requires less power to circulate liquid than open type. (less than 50%)
- Easy to repair as the system components are installed in the machine room.
- The closed system is independent of the ground conditions when installed.
- Relatively low maintenance cost with high efficiency.
- Installable regardless of the presence or absence of groundwater and water quality problems.
Components of a geothermal heating and cooling system
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
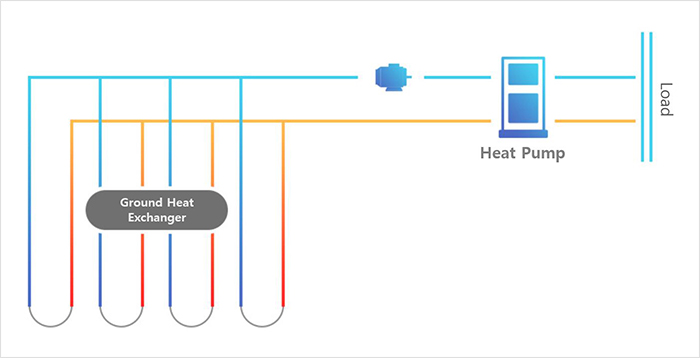
After drilling more than 100m in the ground and inserting HDPE into the hole, heat exchanges between the heat in the ground and the fluid through the fluid inside. The pipe to be inserted must not have problems such as leakage or corrosion and must maintain physical and chemical properties for over 50 years.
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
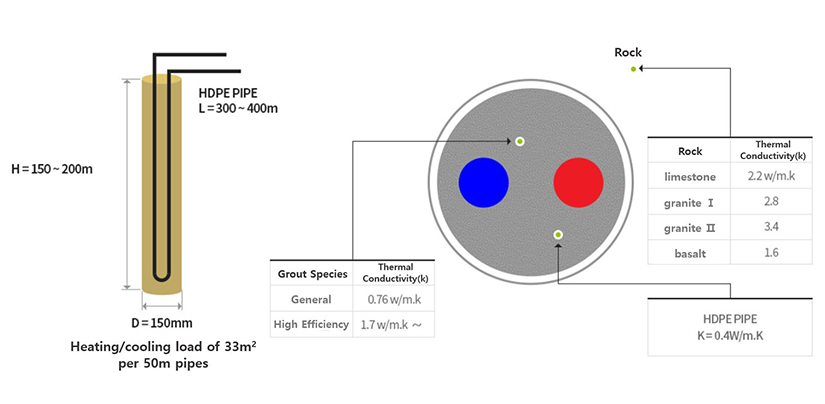
It is a circulation pump to circulate the working fluid of the geothermal system.
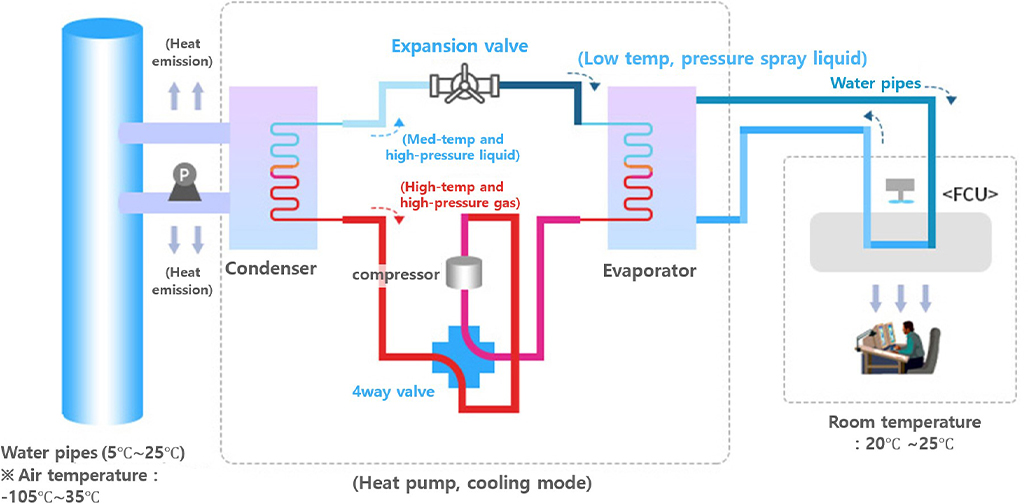
It is a vital component of the geothermal system that absorbs heat from the ground or emits indoor heat to keep the indoor temperature constant, which consists of an expansion valve, heat exchanger, compressor, and 4-way valve.
It determines the operation and abnormalities of the geothermal system, monitors the operation of the geothermal system, and stores and analyzes the measured data to determine the system status.
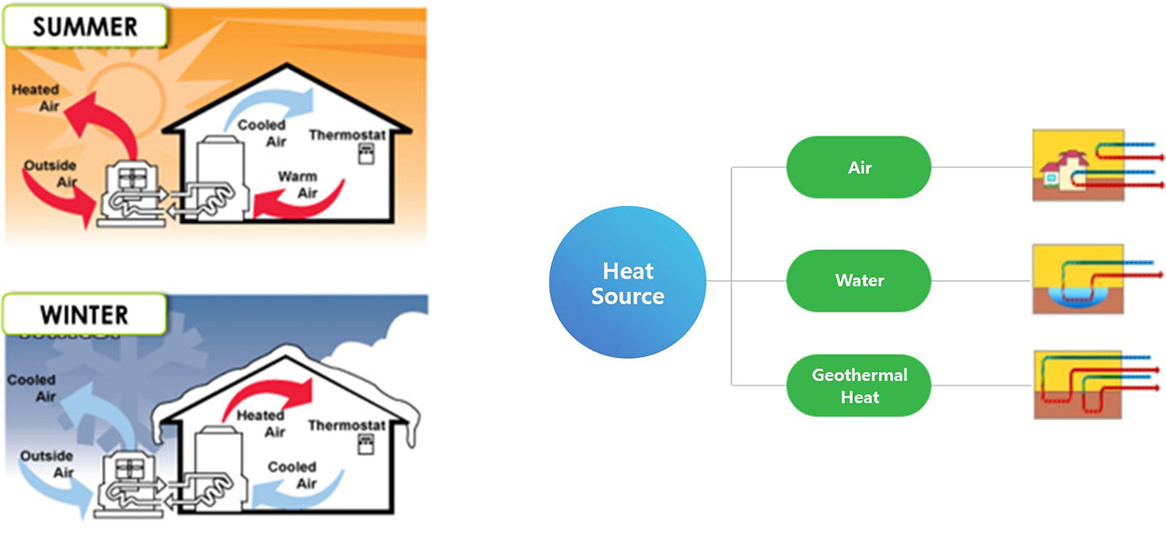
Definition and types of heat pump
- A device transferring heat from a low-temperature area to a high-temperature area
- Release or absorb heat through the process of compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation of the refrigerant
- Available for cooling and heating with a single device
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
Heat pump performance
| Division | Cooling | Heating | Performance (COP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air conditioner |
|
- | 2.5 |
| Air source Heat Pump |
|
|
summer : 2.5 winter : 1.5 |
| Geothermal source Heat Pump |

|
|
summer : 4.0 winter : 3.5 |
Operational principle of geothermal heating and cooling system
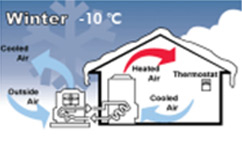
- Cooling: Absorbs the indoor temperature, which has risen due to the outside temperature in summer, and circulates it through the ground heat exchanger to release heat.
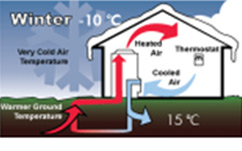
- Heating: The indoor temperature, cooled by the outside temperature in winter, absorbs the heat from the ground and circulates it through the ground heat exchanger to heat the room.
[Conceptual diagram of geothermal heat pump cooling and heating]
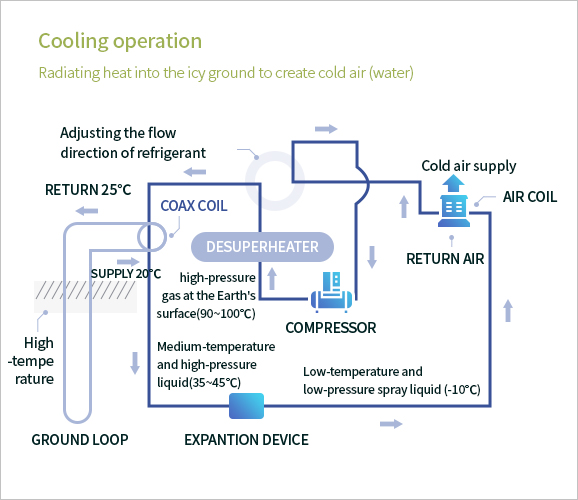
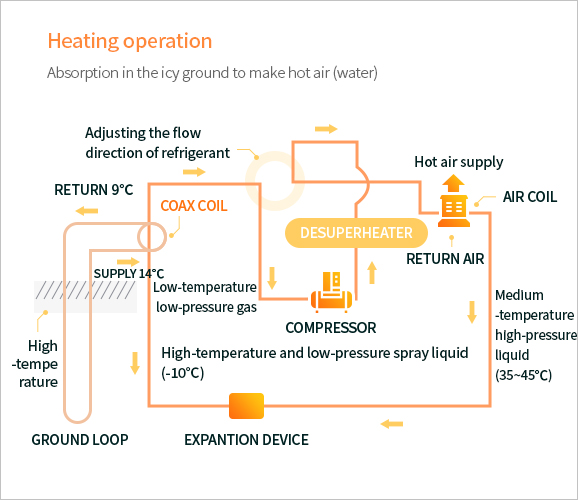
Heating and cooling operation flow chart of geothermal system
[Cooling operation flow chart of geothermal system]
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
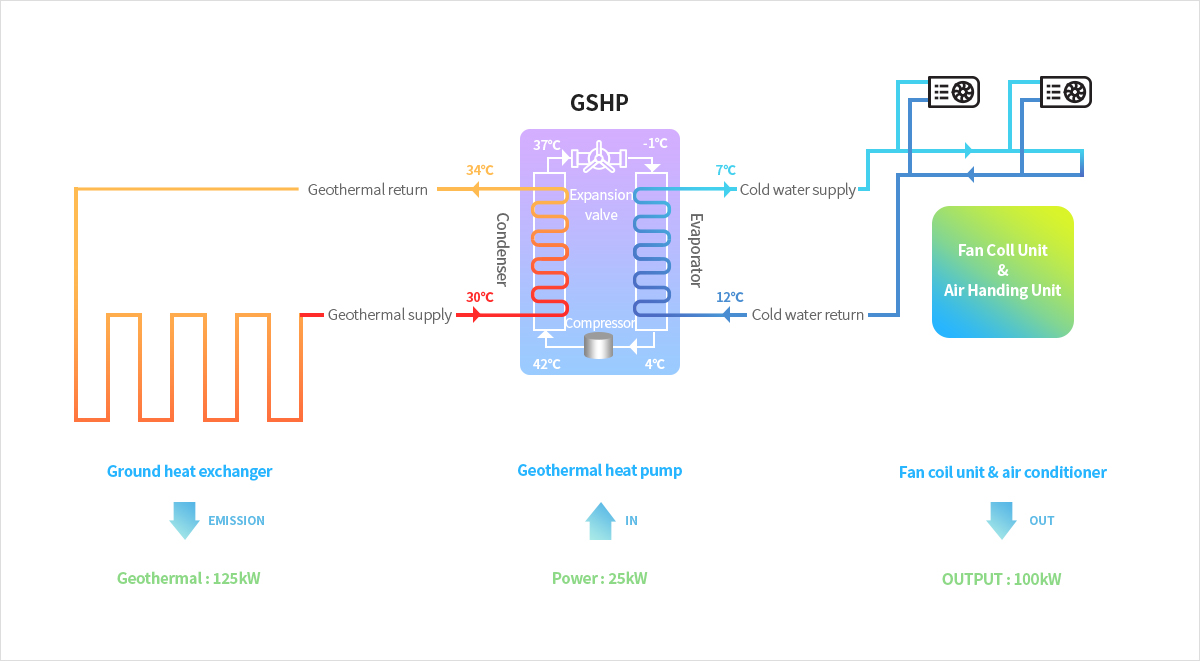
[Heating operation flow chart of geothermal system]
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
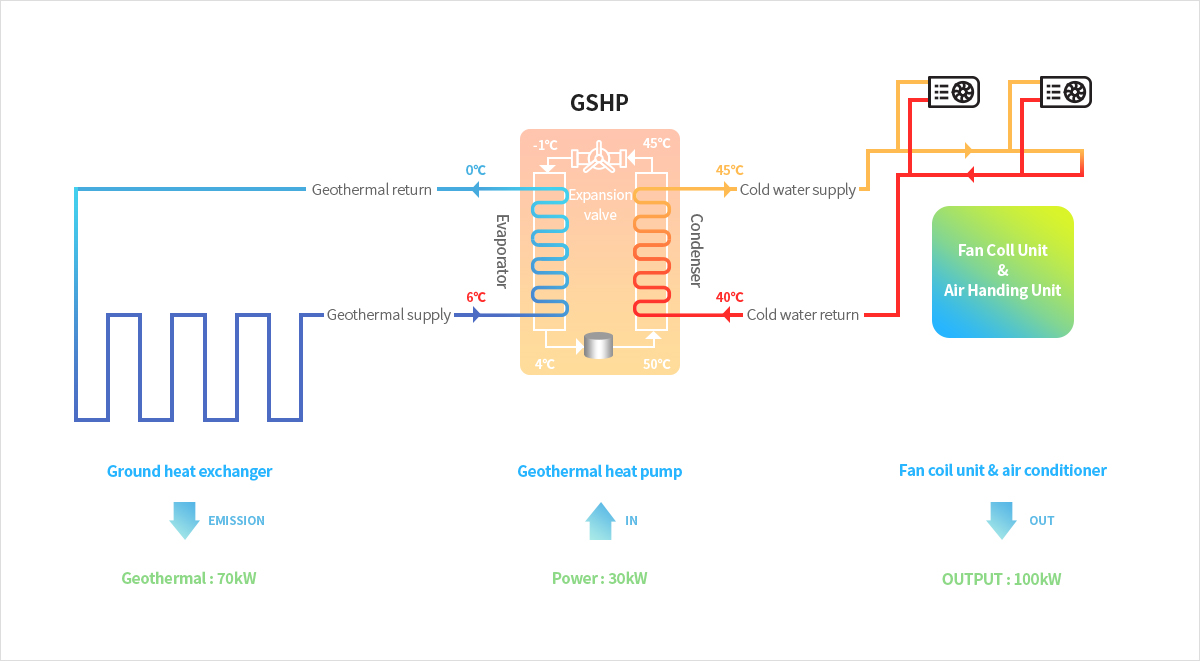
Required area and volume of geothermal heating and cooling system
[Required area and volume]

- Floor area : 3,300㎡ (35,600 ft2)
- 100 RT geothermal system
- Air conditioning height 2.7m
| Division | Building | Ground heat exchanger | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Floor area (m2) | 3,300 | 1,224 | 37% |
| Volume (m2) | 9,900 | 183,600 | 1,850% |
An underground heat exchanger equivalent to about 20 times the total volume is required
Economics of geothermal heating and cooling systems
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
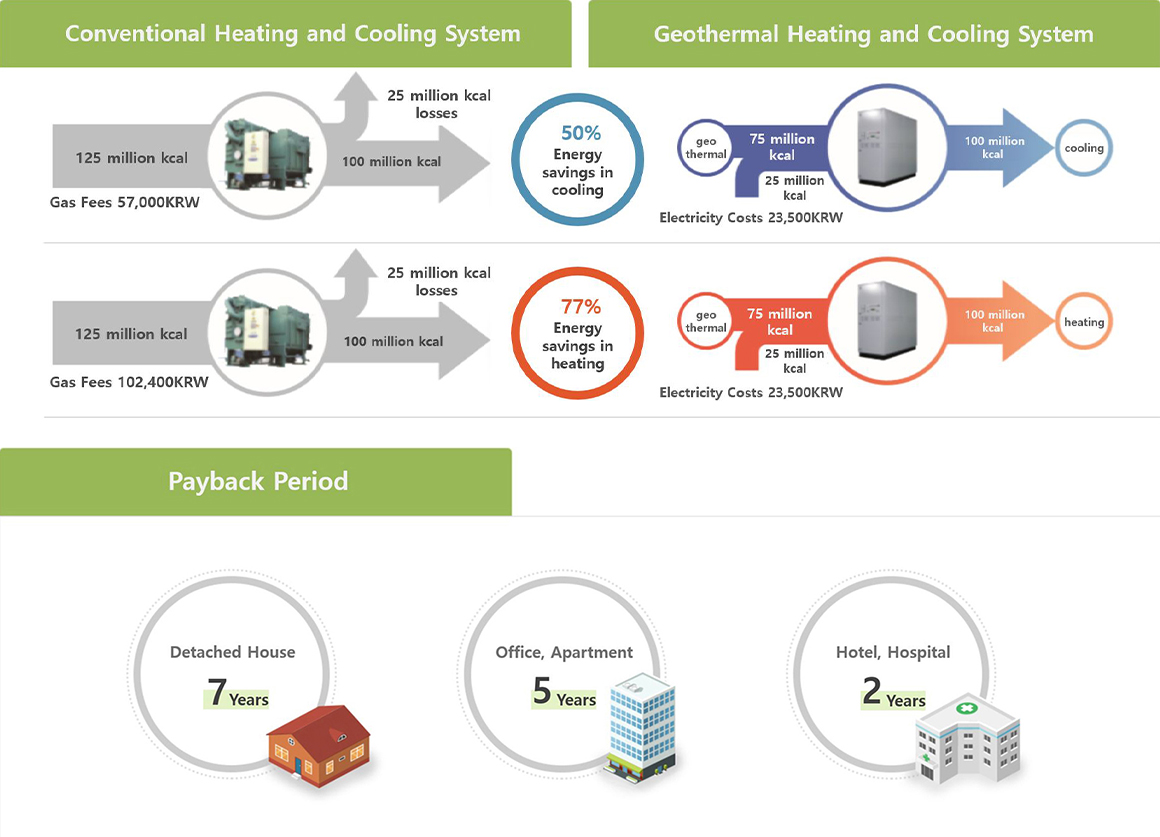
Comparison of geothermal heating and cooling and geothermal power generation
[District heating of Apt Neuroscience]
[Pohang Geothermal Power]
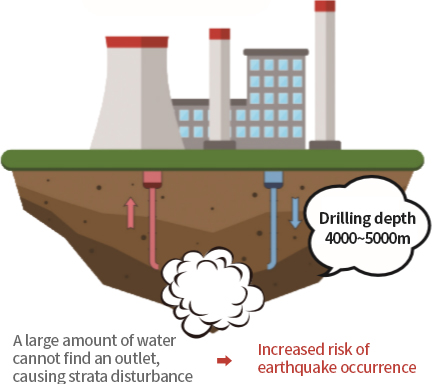
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
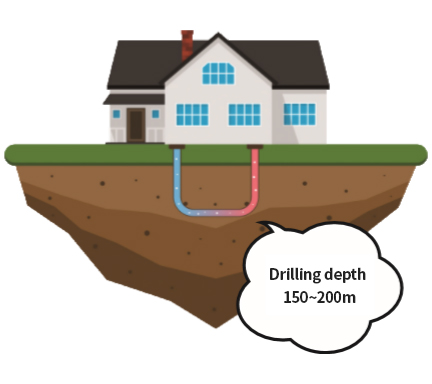
| Feature | A 150-200m underground heat exchanger is installed vertically to absorb and dissipate heat through fluid circulation in the PE pipe. | 4,000~5,000m deep underground is drilled vertically, water is injected to crush the stratum, and high-temperature steam is obtained to produce electricity at power plants on the ground. |
| Production method | Indirect heat exchange only with the ground at a constant temperature throughout the year (average 15°C) | Direct use method to extract high temperature (over 100°C) from deep underground |
| Scope of application | Applicable to all areas of Korean geology | Precise investigation of geological conditions must be preceded. |
| Market status | Expanding the market to more than 200 domestic cases/year and 100,000 overseas cases/year | Used in volcanic layers such as the Nordic volcanic zone, but decreasing due to environmental problems. |
Advantages of geothermal heating and cooling systems
One of the most efficient heating and cooling systems used by mankind
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.

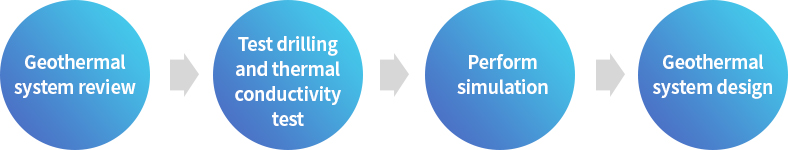
Design of geothermal heating and cooling systems
[Test drilling and thermal conductivity test]
- Thermal response test to measure the thermal conductivity of the ground required for the design of the geothermal system
- Test drilling and underground thermal conductivity tests are to verify the feasibility of the basic geothermal design and determine the final geothermal system specifications.
- Measured based on the gradient of the temperature change of the fluid circulating inside the heat exchanger and dissipating to the ground while injecting a specified heat load into the test hole and the amount of heat injected.
- Submit a geothermal utilization review that reflects the test drilling and thermal conductivity test results to receive evaluation and approval in accordance with the detailed implementation guidelines for the geothermal utilization review in “Guidelines for Support of New and Renewable Energy Facilities, etc.”
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
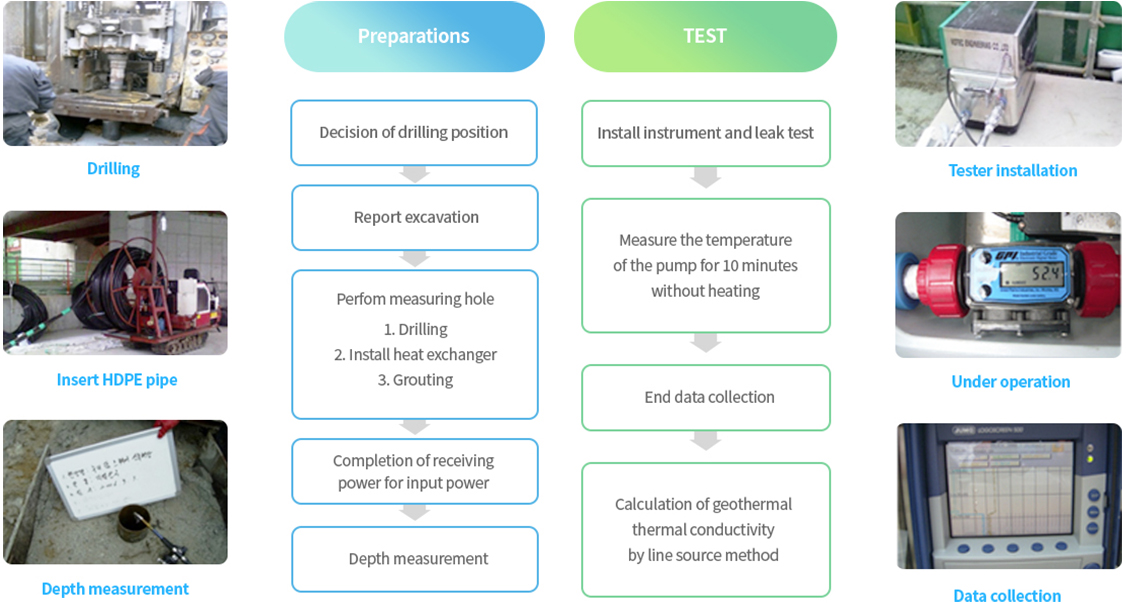
[Underground thermal conductivity test measurement procedure]
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
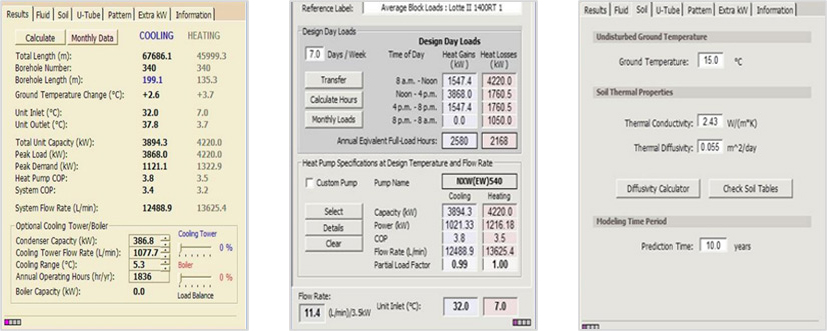
[System design through simulation]
- Calculation method : Conduct simulation reflecting underground conditions, load conditions, and heat exchanger conditions
- Applicable programs : GLD (vertical, horizontal), GLHE Pro (vertical, SCW)
- 63 factors reflected, including underground thermal conductivity (K-Value)
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
Introduction to Apt Neuroscience's Hydrothermal cooling and heating system
Definition of Hydrothermal Energy

A technology that uses water such as surface seawater and river water
as a heat source for heating and cooling directly or using a heat pump.
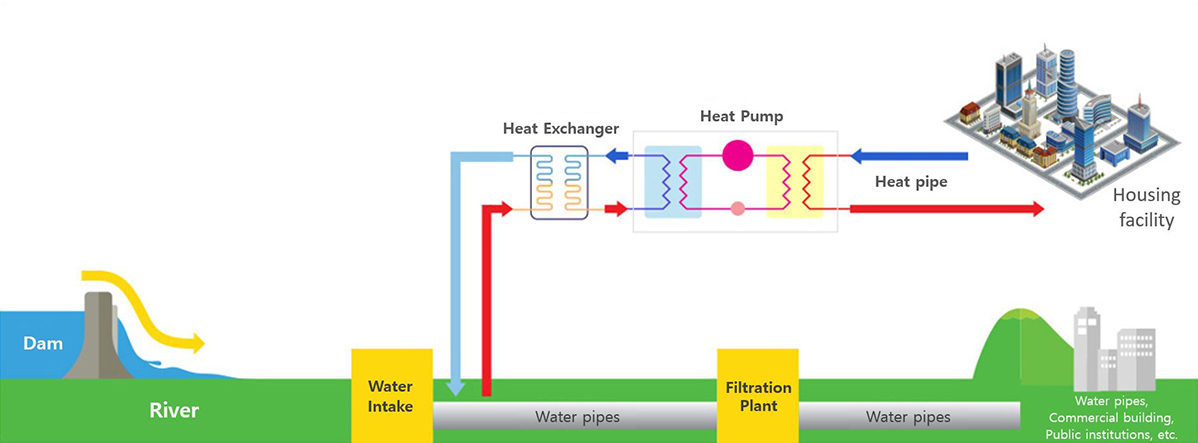
Hydrothermal heating and cooling system
A system that recovers the temperature energy of water directly or with a heat pump for cooling and heating the building.
Using the temperature energy of water, the heat in the building is released to water resources during cooling, and heat is obtained from water sources and supplied to the room while heating.
Operational principle of hydrothermal heating and cooling system
- Cooling: Absorbs the indoor temperature, which is elevated by the outside temperature in summer, and releases heat to the heat-receiving side.
- Heating: The indoor temperature cooled by the outside temperature in winter is absorbed by heat from the water heating side to heat the room.
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
Advantages of hydrothermal heating and cooling systems
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
The temperature fluctuation in summer and winter is small compared to the air temperature
Energy savings by about 20 to 50% compared to conventional fossil fuels
Can develop at low cost when using existing water pipelines
Abundant resources available from nearby raw water pipelines, rivers and dams
Resolving the urban heat island effect by avoiding noise from cooling towers and not using outdoor units
Introduction to Apt Neuroscience's Solar Energy System
Definition of Solar Energy System

Solar Energy System is a power generation technology that produces
electricity by directly converting the light energy of the sun, and uses
solar cells that generate electricity by the photoelectric effect
when sunlight is received.
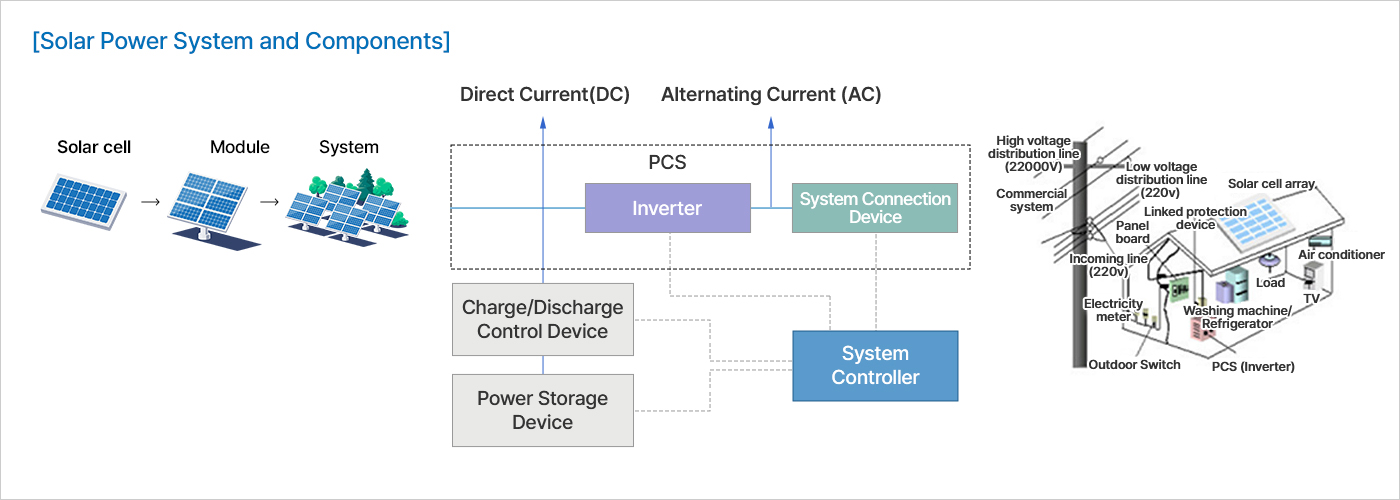
Components of Solar Energy System
Solar Energy System consists of a photovoltaic module corresponding to a generator,
a power storage device with a power storage function, a power converter (PCS, Power Conditioning System)
that converts direct current generated from solar cells into alternating current, system control and monitoring, and a load.
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
Principles of Solar Energy System
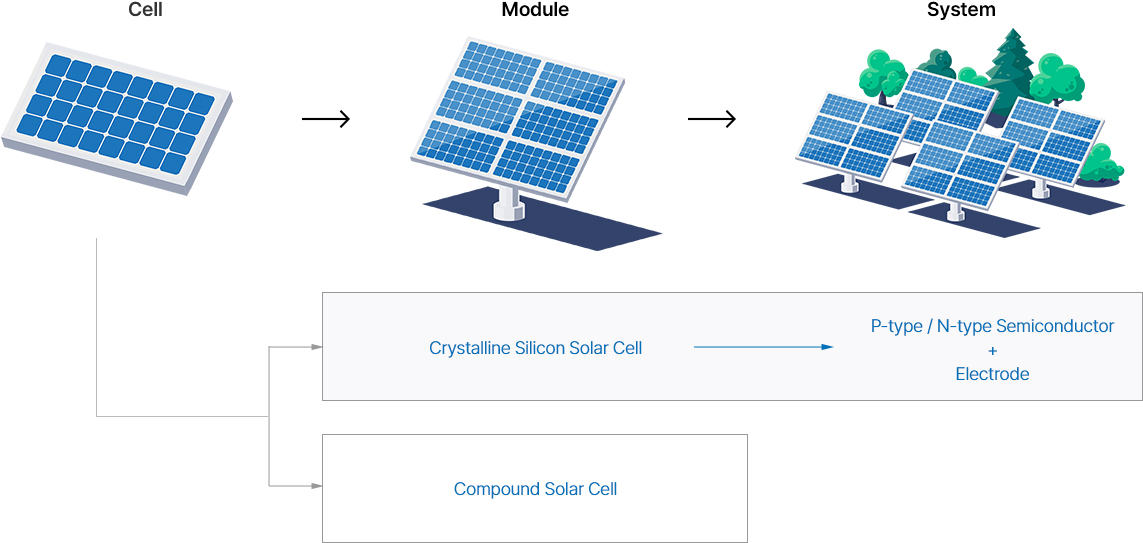
Solar cells, Modules, and Systems turn sunlight into electricity through their respective roles In Solar Energy System.
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
[Principes of Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells]
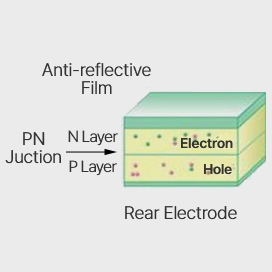
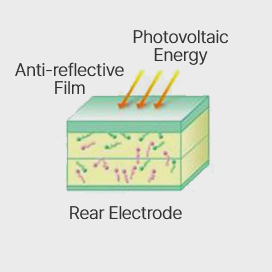
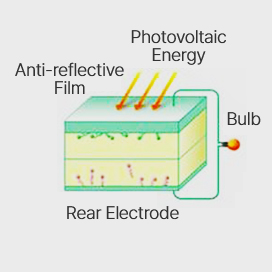
① A crystalline silicon solar cell has a structure in which an N-type semiconductor and a P-type semiconductor with different electrical properties are bonded together.
The boundary between the two semiconductors is called a PN junction, and an electric field is formed in the solar cell by the PN junction.
② When sunlight shines on a solar cell, electrons (-) and holes (+) are created. These electrons and holes roam freely and do not generate electricity.
③ While moving freely inside the semiconductor, when the electric field created by the PN junction enters,
electrons (-) stick to the N-type semiconductor and holes (+) stick to the P-type semiconductor. At this time, when electrons flow to an external circuit by forming electrodes on the surfaces of the P-type and N-type semiconductors, current is generated.
Supply types of Solar Energy System

Large-Scale Solar Power Plant

Floating Solar Power

Roof Solar Power
Advantages of Solar Energy System
The energy source is clean and unlimited.
It is possible to generate the necessary amount of electricity in the necessary place.
Maintenance is easy and unmanned is possible.
It has a long lifespan (about 20 years or more).
Introduction to Apt Neuroscience's fuel cell system
Definition and Principle of Fuel Cell
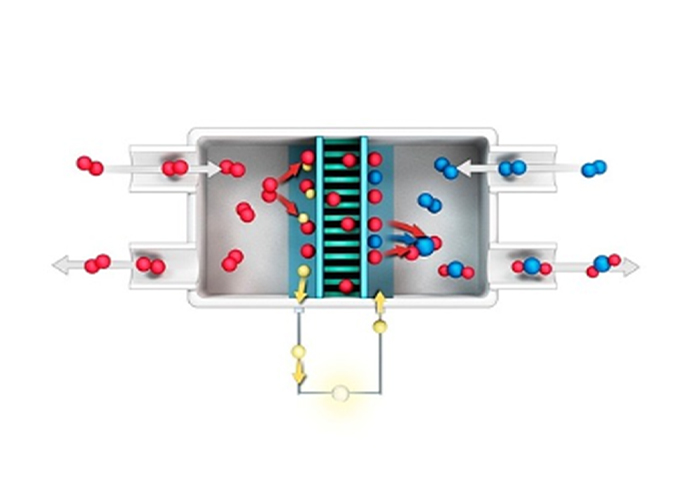
-
Electrolysis of water produces hydrogen and oxygen.
On the other hand, a fuel cell is an electrochemical generator that produces electricity from hydrogen and oxygen. - High-efficiency eco-friendly power generation system that simultaneously produces electricity and heat (hot water) using city gas
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
- Anode reaction : H2 → H+ + 2e-
- Cathode reaction : 1/2O2 + 2H+ + 2e- → H2O + Heat
- Total Reaction : H2 + 1/2O2 → H2O
What is a fuel cell?
High-efficiency eco-friendly power generation system
that simultaneously produces electricity and heat (hot water) using city gas
- 5kW : 1.35N㎥ of city gas = 5kWh of electricity + 150L of 60℃ hot water (per hour)
- 10kW : 2.6N㎥ of city gas = 10kWh of electricity + 150L of 60℃ hot water (per hour)
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
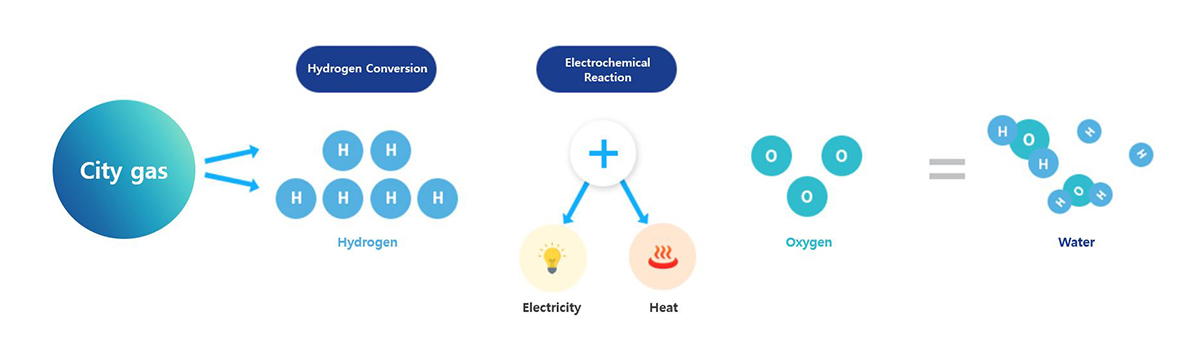
- Electricity and heat are produced through a chemical reaction between hydrogen in city gas and oxygen in the air
(generation efficiency 30-40%, thermal efficiency 50%, total 80-90%) - Available 365 days a year (ON/OFF possible)
Feature of fuel cell
- 30~40% electricity generation efficiency, over 50% thermal efficiency, total high efficiency of 80~90%
- Low-emission energy system due to no combustion process in thermal or diesel power generation
- Easy to adjust the power generation scale because it can be manufactured in the form of a module
- Fewer restrictions on the installation area
- Less noise and noxious gas emissions
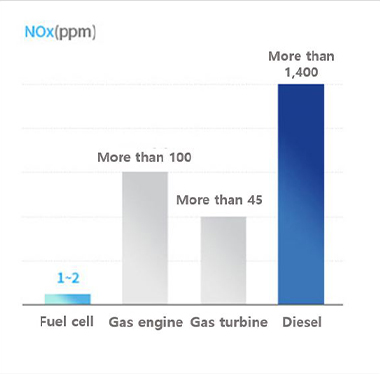
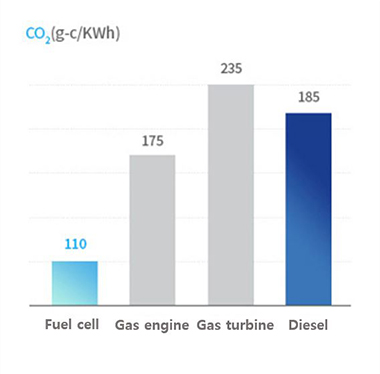
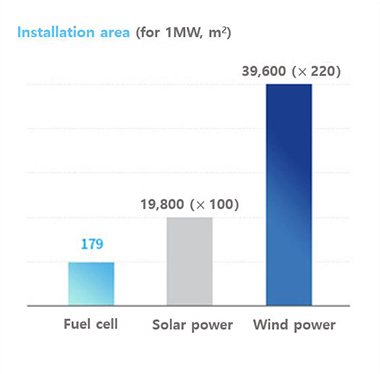
Source : poscoenergy, Meritz Securities Research Center
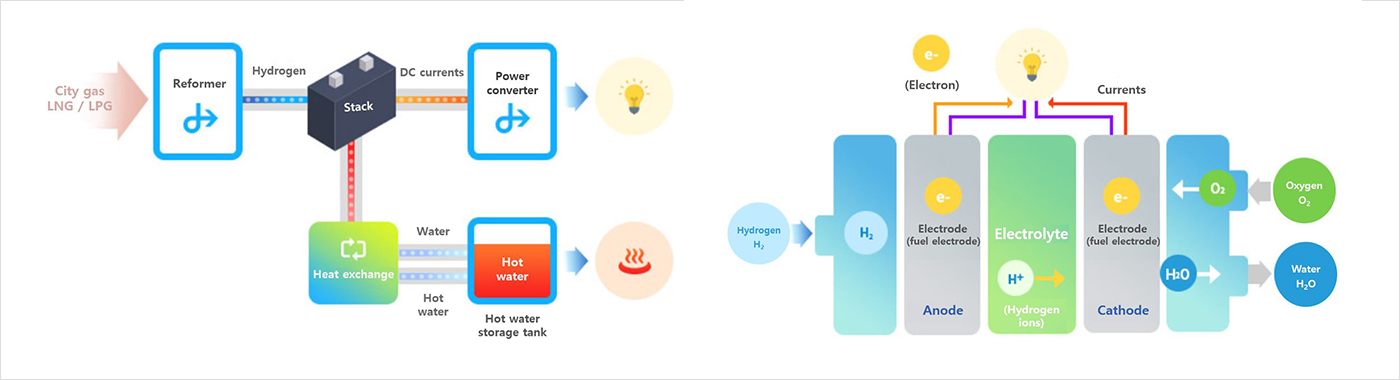
Composition of fuel cell
- The fuel cell system consists of a fuel processing module, stack module, power conversion module, and heat treatment module
- Hydrogen generated through the reformer and air supplied by the air blower react in the stack to produce electricity and heat
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
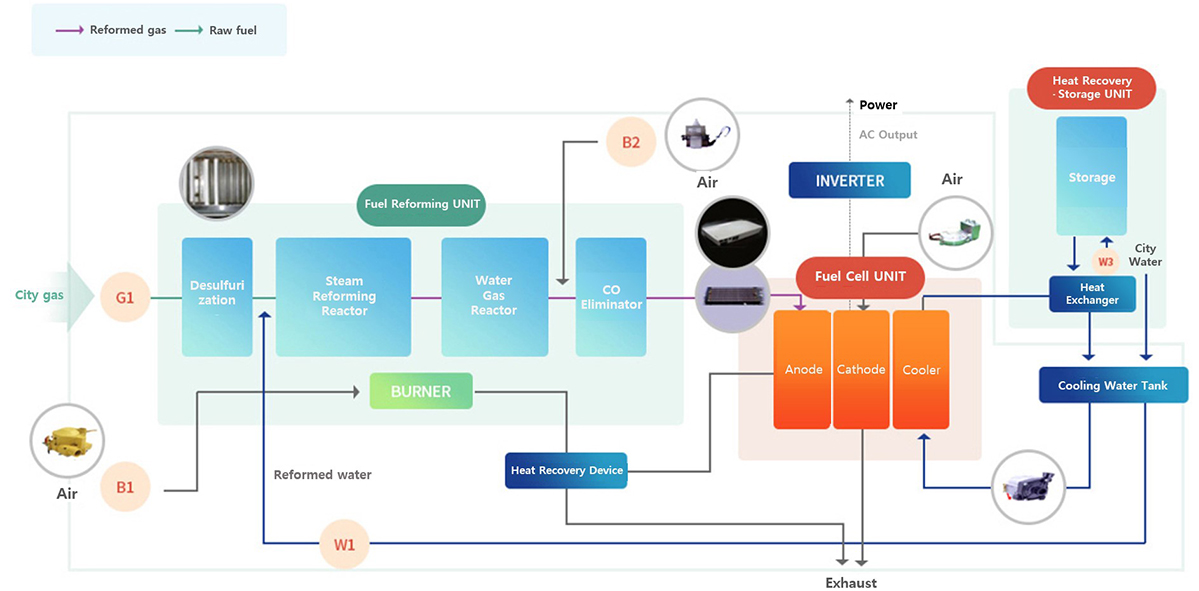
| Division | Device | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Generation unit | Fuel processing unit | A device that separates hydrogen from city gas |
| Fuel cell stack | A critical component that produces electricity and heat through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen | |
| Power converter | A device that converts direct current electricity in a fuel cell into alternating current electricity | |
| Heat recovery unit | Waste heat recovery unit | A device that separates hydrogen from city gas |
| Fuel cell stack | A critical component that produces electricity and heat through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen |
Composition of fuel cell
- The stack is a key part such as the engine of gasoline power generation in fuel cells.
- It is composed of stacking several unit cells (Cells) in series, and the generated current is proportional to the area of the cell and the voltage to the number of stacked cells.
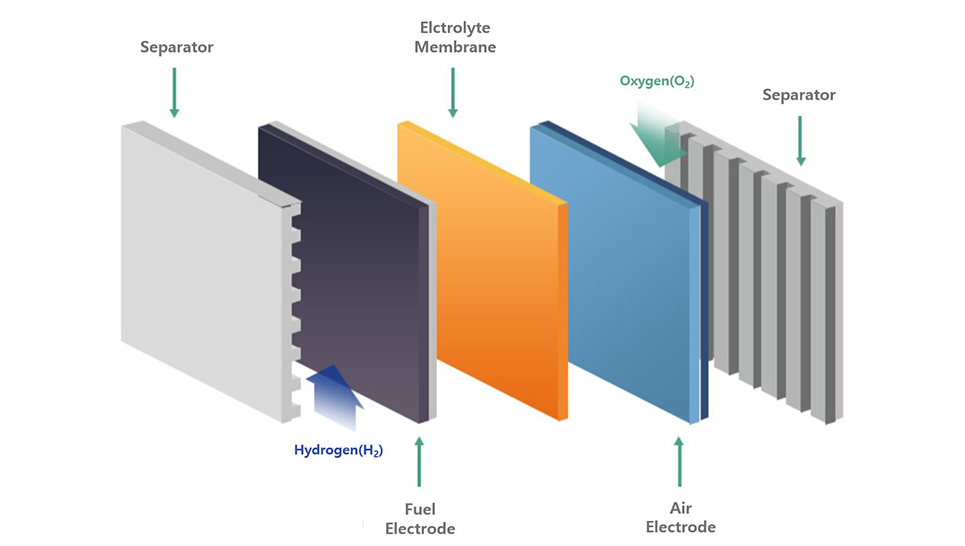
- A cell consists of an electrode assembly (MEA: Membrane-Electrode Assembly), a gas diffusion layer (GDL), and a separator plate.
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
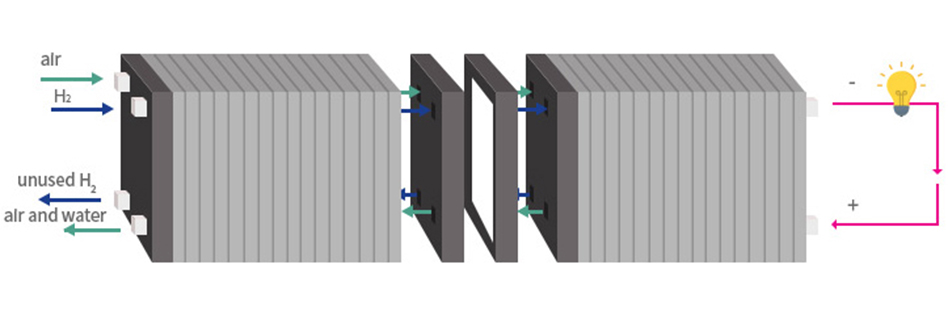
[Fuel Cell Structure]
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
Types of Fuel Cells
- Fuel cells are classified according to the type of electrolyte and operating temperature.
- FEMFC has the highest level of perfection and is currently commercialized and supplied to households and buildings.
- MCFC and PAFC are used for MW class large power generation.
- SOFC, which has the advantage of using the highest efficiency and various fuels, can be widely used for the household to large-scale power generation, so the most active research is underway.
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
| Division |
Alkali (AFC) |
Phosphate type (PAFC) |
Molten carbonate type (MCFC) |
Solid oxide type (SOFC) |
Polymer electrolyte type (PEMFC) |
Direct methanol (DMFC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte | Alkali | Phosphate | Carbonate | Ceramic | Ion exchange membrane | Ion exchange membrane |
| Working temperature (℃) | below 120 | below 250 | below 700 | below 1,200 | below 100 | below 100 |
| Efficiency (%) | 85 | 70 | 80 | 85 | 75 | 40 |
| Usage | Space projectile power | Medium-sized building (200kW) |
Medium/large building (100kW~MW) |
Small/medium/large-capacity power generation (1kW~MW) |
For home/commercial use (1~10kW) |
Mobile (below 1kW) |
| Feature | - |
High CO durability, cogeneration response possible |
High power generation efficiency, internal reforming possible, cogeneration response possible |
High power generation efficiency Internal reforming possible, combined power generation possible |
Low temperature operation, high power density |
Low temperature operation, high power density |
Source: Korea Energy Management Corporation, Meritz Securities Research Center
Introduction to fuel cell system


You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
| Fuel used | City gas | City gas | City gas | City gas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimension(mm) | 500 x 400 x 900 (W x D x H) | 500 x 700 x 1,550 (W x D x H) | 1,400 x 650 x 1,520 (W x D x H) | 1,400 x 650 x 1,520 (W x D x H) |
| Gas consumption(Nm3) |
0.16(Normal 0℃) 0.18(Standard 25℃) |
0.26(Normal 0℃) 0.28(Standard 25℃) |
0.3 (Normal 0℃) 1.5(Standard 25℃) |
2.6(Normal 0℃) 2.8(Standard 25℃) |
| Power generation/thermal efficiency (%_LHV) | 35/50 | 35.2/ 51.67 | 36.6 / 49.1 | 37.8 / 52.2 |
| AC 220v, Single phase 2 wire | AC 220v, Single phase 2 wire | AC 220v, Single phase 2 wire | AC 220v, Single phase 2 wire | AC 380v, 3-phase 4-wire |
| Heat storage tank capacity(L) | - | 125 | 220 | 450 |
Photo of fuel cell installation

Electricity
The electricity produced from the fuel cell is connected to the grid with KEPCO
and used as a base load for buildings, and electricity costs are saved by using
it in parallel with KEPCO.
In case of shortage, additional grid electricity from KEPCO are brought for use.
Heat
The heat produced by the fuel cell heats the domestic hot water in the building,
flows into the boiler, and supplies it to the hot water users (toilet, restaurant, etc.)
to save heat charges.
Introduction to Apt Neuroscience's Main Experiences
Geothermal heating and cooling system, No. 1 market share
Establishment of a trust system by continuously winning orders from major domestic landmarks (80%) and the public sector
Received orders for 10 major geothermal projects in Korea, including FED communication center

LOTTE World Tower

Seoul Government New Complex

Sejong Government Complex

KEPCO New Office Building

Incheon International Airport Phase 3

Gyeongbuk Regional Government Complex

Samsung R&D Center

Naver 1784 (The 2nd Office Building)
Research Project (Company-Affiliated Research Institute)
Development of urban mass renewable energy hybrid heat supply smart platform
>Development of smart design and operation platform for urban mass hybrid heat supply with
3 or more types of renewable energy heat sources and 30% or more of supply
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
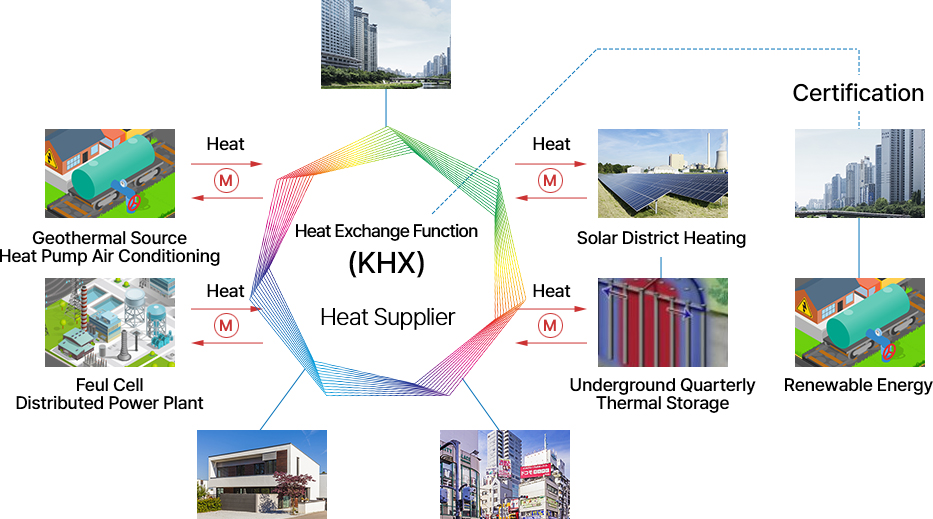
[Development of technology for building an energy sharing community based on low-carbon energy efficiency technology]
Due to the installation of the regulatory sandbox,
two community and city integration demonstrations and early commercialization
targeting a smart city demonstration city (Siheung City) and a smart city national pilot city (Busan EDC)
that can create a new energy sharing ecosystem
Establishment of a sustainable smart energy sharing community
and creation of an energy welfare ecosystem by making business model
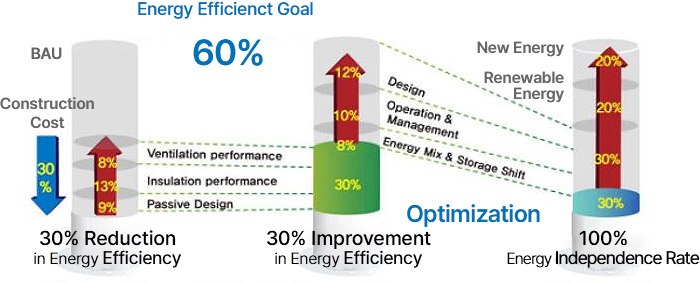
Energy efficiency improvement 60%, Creation of Net Zero Energy Community
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
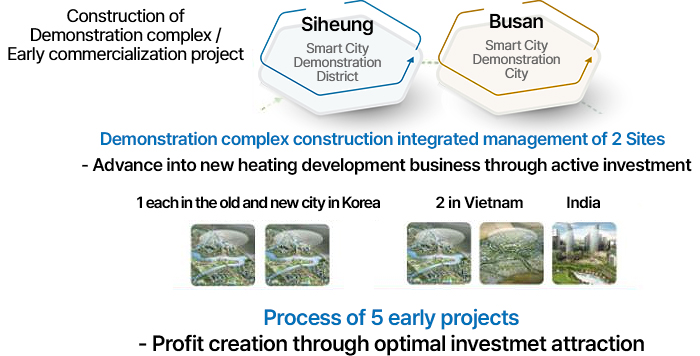
Establishment of 2 Demonstration complexes, 5 early commercialization projects
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
Cloud SHARE
- Smart Sensor
- Smart City Platform
- Clean Energy
- Unified S/W Tool
- Total Energy Solution
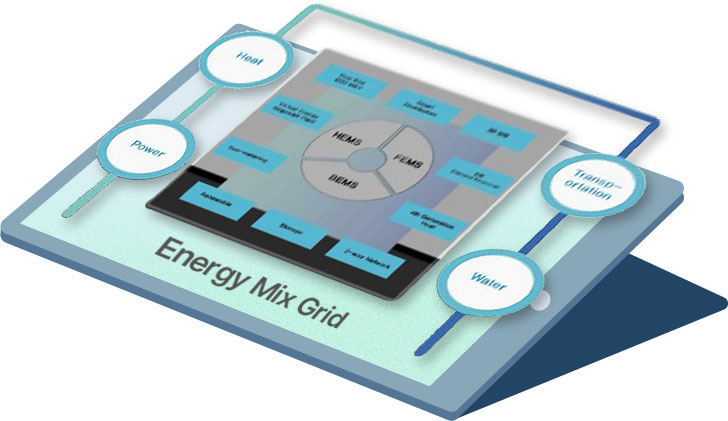
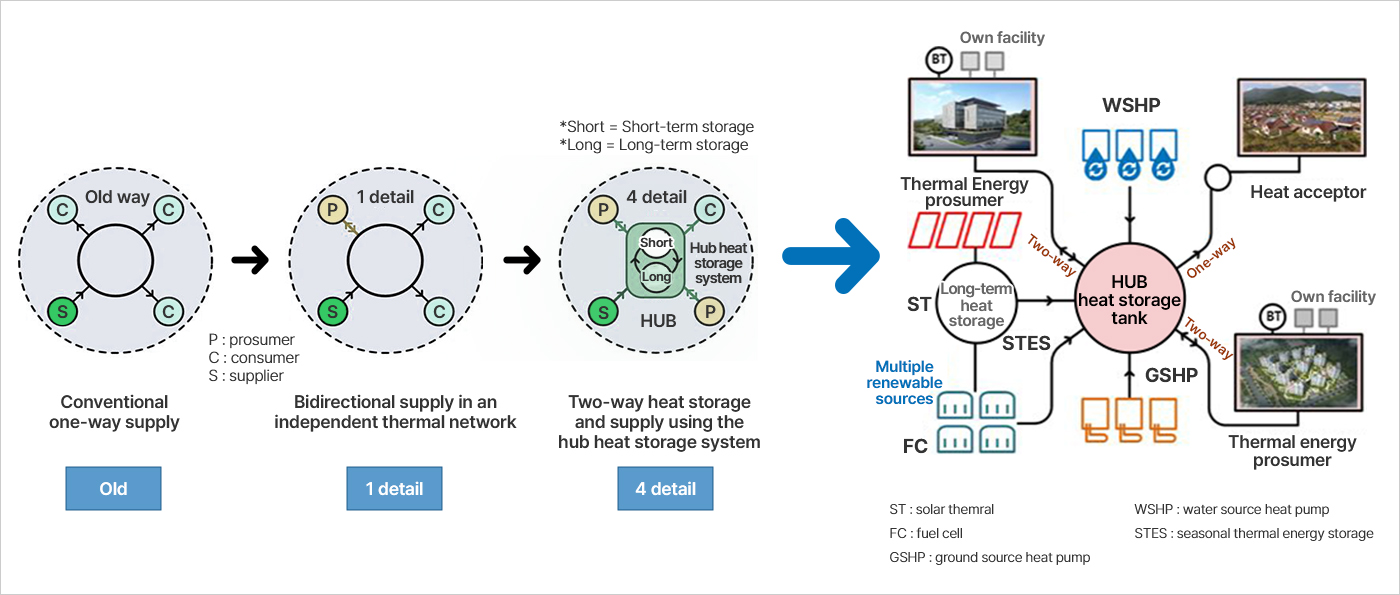
[Development of complex and distributed smart hub heat storage system for heat transaction]
A smart hub heat storage system that stores heat energy produced from various heat sources,
including renewable and unused energy, and supports two-way heat transaction between multiple heat energy prosumers
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
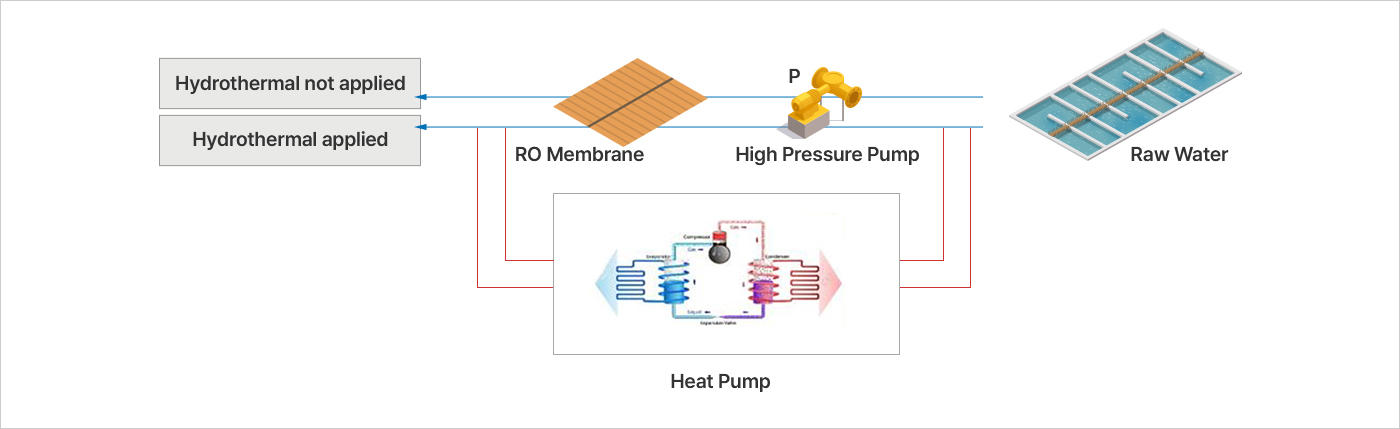
[Development of water treatment process improvement technology using hydrothermal energy]
Development of a standard membrane filtration water treatment process with hydrothermal application
through the development and demonstration of a membrane filtration plant complex utilization operation system for greenhouse gas reduction
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
You can view and view the sushi horizontally.
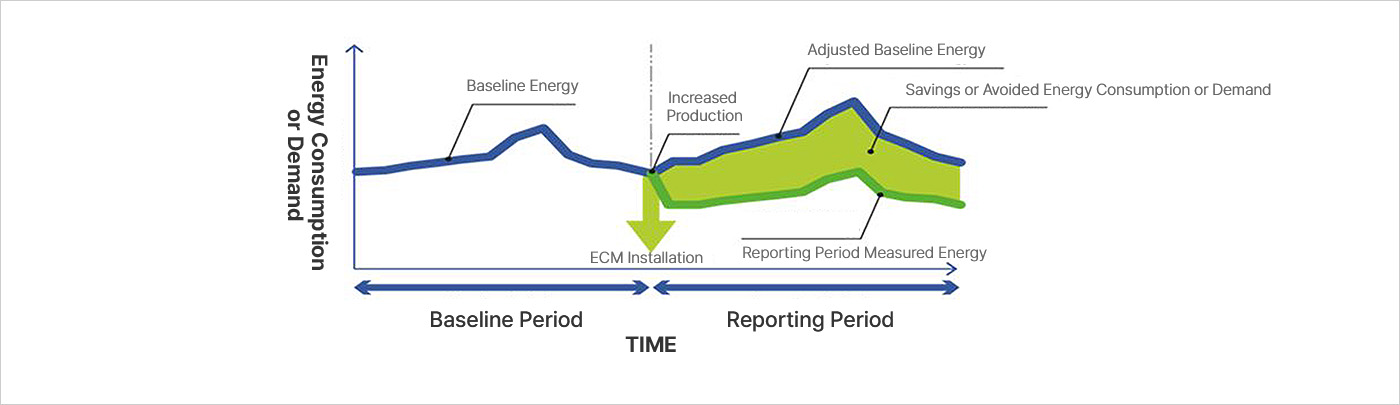
[Development of active high-efficiency hybrid heat pump system for effective utilization of hydrothermal energy]
- Development of active heat source control optimal operation controller
- Development of high-efficiency hydrothermal hybrid cooling and heating heat pump system
- Development of a high-efficiency hybrid heat pump systemthat can link complex heat sources
- Korean hydrothermal/geothermal source heat pump cooling and heating partial load performance coefficient (IPLV)
- development system simulation and economic evaluation
[Commercialization of eco-friendly and high-efficiency combined heat source cooling and heating systems using hydrothermal energy]
Securing system stability and performance through design/construction/operation technology development
and empirical evaluation and
certification/verification for the commercialization of eco-friendly and
high-efficiency combined heat source cooling and heating systems using hydrothermal energy
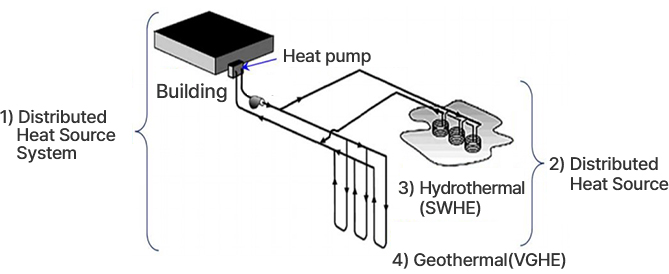
- 1) A heat pump system using a distributed heat source and a cooling/heating system using a distributed heat source have the same concept
- 2) Distributed heat source: geothermal and hydrothermal combination
- 3) Hydrothermal or hydrothermal heat exchanger: utilization of river water
- 4) Geothermal heat or geothermal heat exchanger: (VGHE, Vertical Geothermal heat Exchanger)

